CLNG champions public policies that advance the production of LNG in the U.S., increase international exports, and help power a clean energy future. The United States has vast deposits of natural gas, enough to last several generations even without any of the massive technological breakthroughs that have regularly occurred in the natural gas industry throughout history.
WHAT IS LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to 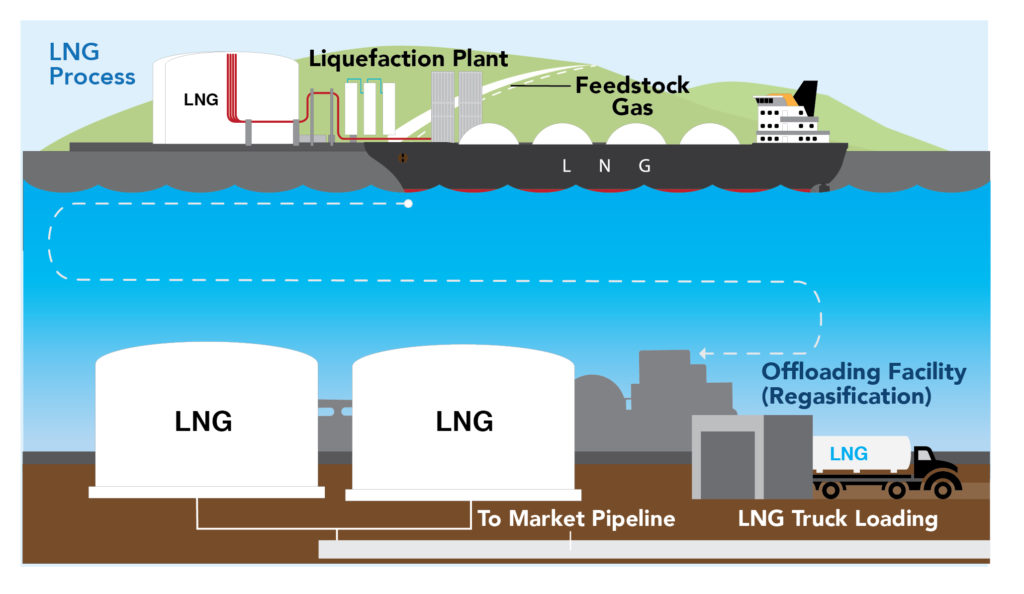 about -260 degrees Fahrenheit, which reduces its volume and makes it easier to transport.
about -260 degrees Fahrenheit, which reduces its volume and makes it easier to transport.
- Liquefying natural gas reduces its volume so much that some of the largest ships that transport U.S. LNG to our international trading partners can carry enough natural gas to power 70,000 homes for one year.
Once at its destination, LNG is regasified and made available for a variety of uses.
- Most commonly, it supplies natural gas to power plants to generate electricity or provides fuel for heating and cooking in residences and businesses.
- It is also used to manufacture steel, glass, paper, brick and many other products.
- Natural gas is also used as a raw material in common products such as medical equipment, paint, fertilizer, cosmetics and plastics.
THE LNG JOURNEY
- Natural gas travels by pipeline to a liquefaction facility.
- Molecules that freeze at low temperatures, like water, carbon dioxide and heavier hydrocarbons, are then removed.
- The remaining gas is cooled to about -260 degrees Fahrenheit, at which point the gas becomes a liquid.
- The LNG is then loaded onto LNG cargo ships for transport. Some of the largest LNG ships or tankers can carry enough natural gas to power 70,000 homes for one year.
- When the LNG reaches an offloading facility, it may be “warmed” or regasified and then transported by pipeline to power plants for use in power generation; or to industrial facilities to manufacture goods; or homes and office buildings for heating, cooking and drying clothes.
AMERICA’S LNG OPPORTUNITY
America’s vast abundance of natural gas has positioned us as the world’s leading exporter. We began to export LNG internationally in 2016 and the U.S. is now the world’s largest exporter.
LNG exports create economic opportunity, revenues and jobs here at home, while raising people out of energy poverty internationally and making their air cleaner and easier to breathe.
- In just a few short years, the U.S. has become the world’s largest LNG exporter by volume, providing cleaner, affordable, abundant energy to more than 37 countries.
- As of April 2025, the United States has 8 existing LNG export facilities, another 8 approved by FERC and under construction, and an additional 12 that have received FERC approval but have not started construction. (See FERC’s map of existing and proposed LNG terminals here.)
